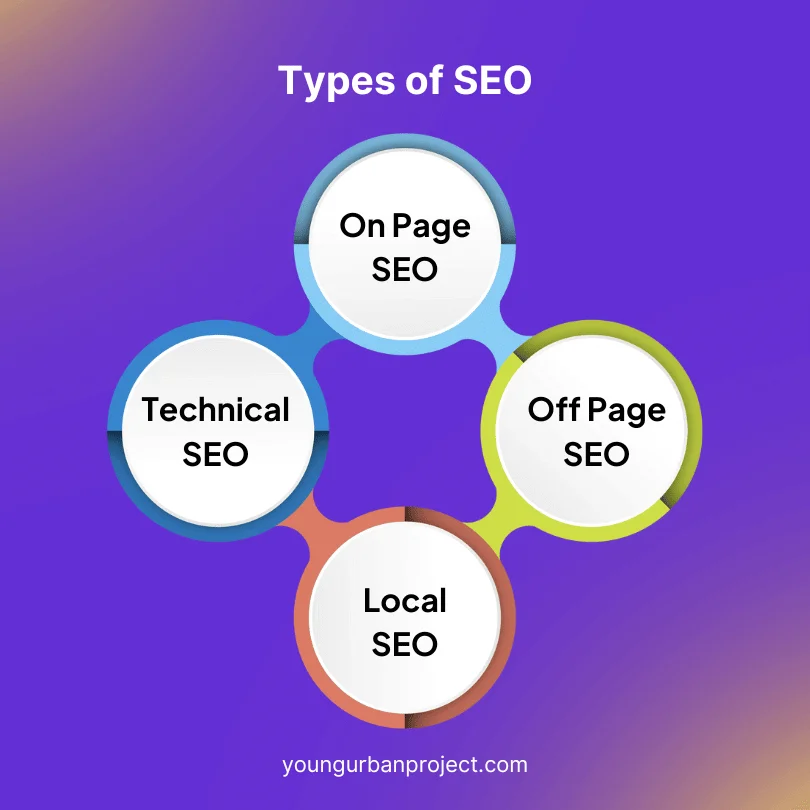
The Three Core Types of SEO
1. Technical SEO
The Foundation. This is the work done to make your website easy for search engines to crawl, access, and understand. If your technical SEO is poor, search engines will struggle to index your content, making all other SEO efforts less effective.
Key Focus Areas:
- Crawlability: Ensuring search engine bots can easily navigate your site (e.g., a good
robots.txtfile, a logical site structure). - Indexing: Making sure search engines can add your pages to their database. This involves proper use of meta tags (like
noindex) and avoiding duplicate content. - Site Speed: Optimizing page load times for both users and bots.
- Mobile-Friendliness: Having a responsive design that works perfectly on all devices.
- Site Architecture: A logical, flat site structure that makes it easy for users and bots to find important content.
- Security (HTTPS): Using a secure protocol to protect user data.
- Structured Data (Schema Markup): Adding code to your pages to help search engines understand the context of your content (e.g., recipes, events, products), which can lead to rich results.
Analogy: Technical SEO is like building the foundation, plumbing, and electrical wiring of a house. You don’t see it, but the house can’t function without it.
2. On-Page SEO
The Content. This involves optimizing the content and HTML source code of individual pages to rank higher and earn more relevant traffic.
Key Focus Areas:
- Keyword Research & Usage: Identifying the words and phrases your audience searches for and incorporating them naturally into your content.
- Content Quality & Relevance: Creating high-quality, comprehensive, and valuable content that satisfies user intent.
- Title Tags & Meta Descriptions: Crafting compelling and keyword-rich titles and descriptions that appear in search results.
- Header Tags (H1, H2, H3): Using headings to structure your content logically for readability and SEO.
- URL Structure: Creating clean, descriptive, and user-friendly URLs.
- Image Optimization: Using descriptive file names and alt text for images.
- Internal Linking: Linking to other relevant pages on your own site to spread “link equity” and help users navigate.
Analogy: On-Page SEO is like designing the interior of each room in the house—the paint, furniture, and layout—making it attractive and functional for the people inside.
3. Off-Page SEO
The Reputation. This is the work done outside of your own website to improve your site’s authority, trust, and rankings. The most critical factor here is link building.
Key Focus Areas:
- Link Building (Backlinks): Acquiring hyperlinks from other high-quality, relevant websites to your own. This is a major vote of confidence in the eyes of Google.
- Social Signals: While not a direct ranking factor, having your content shared on social media increases its visibility and can lead to natural backlinks.
- Online Mentions & Brand Signals: When your brand is mentioned online (even without a link), it can build recognition and trust.
- Local SEO Listings: For local businesses, this includes managing your Google Business Profile and other directory listings (e.g., Yelp, Bing Places).
Analogy: Off-Page SEO is like your home’s reputation in the neighborhood. Good reviews, recommendations from friends, and a strong presence in the community make people trust and visit your house.
Other Important Classifications
Beyond the three pillars, SEO is often categorized by the type of search results it targets:
1. Local SEO
A subset of SEO focused on optimizing a business to be found in local search results.
- Goal: Appear in the “Local Pack” (the map with 3 business listings) and local organic results.
- Key Activities: Optimizing your Google Business Profile, managing local citations (name, address, phone number), and earning local backlinks and reviews.
2. International SEO
The process of optimizing a website to rank in multiple countries and languages.
- Goal: Reach a global audience.
- Key Activities: Using hreflang tags, choosing the right country-specific domains (e.g.,
.co.uk,.de), and creating culturally relevant content.
3. E-A-T & YMYL SEO
This isn’t a separate type but a crucial concept, especially for On-Page and Technical SEO, that focuses on quality signals.
- E-A-T: Stands for Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness. Google uses this to evaluate the quality of content, particularly for YMYL topics.
- YMYL: Stands for “Your Money or Your Life”—topics that can impact a person’s health, financial stability, or safety (e.g., medical advice, financial news, legal information). For these topics, demonstrating high E-A-T is critical.
Visual Summary: The SEO Funnel
You can think of the three core types working together in a funnel:
- Technical SEO: Ensures search engines can FIND your site.
- On-Page SEO: Ensures search engines can UNDERSTAND your content and that users find it valuable.
- Off-Page SEO: Tells search engines that other people TRUST your content, boosting its authority.
All three types are essential for a successful, long-term SEO strategy. Ignoring one will limit the effectiveness of the others.